Cognitive learning theory plays a pivotal role in modern education, offering insights into how students absorb, process, and retain information. This guide delves into:
- Understanding the foundations of cognitive learning theory
- Exploring examples and applications in the classroom
- Insights into social cognitive learning theory
Read on to empower your teaching strategies and foster a more engaging and effective learning environment.
Understanding Cognitive Learning Theory
What is Cognitive Learning Theory?
Cognitive learning theory delves into the intricate processes of how people understand, learn, and remember information. It posits that learning is not just a passive absorption of information but an active construction of knowledge, where learners engage with content, think critically, and solve problems.
🧠 The theory emphasizes the role of mental activities such as perception, attention, and memory, and it highlights the importance of connecting new information to existing knowledge.
Social and environmental factors are also acknowledged as significant influencers in the learning process, with educators urged to create learning environments that encourage active participation and critical thinking.
Ultimately, cognitive learning theory provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the multifaceted nature of learning, promoting strategies that enhance memory, foster problem-solving skills, and encourage a deeper engagement with learning material.
Understanding cognitive learning theory is like opening a treasure chest of insights into the human mind and its learning processes. It’s based on the idea that learning is more than just a response to external stimuli; it’s an active mental process.
Cognitive Processes at Play
- Memory and Recall: When new information is presented, our brains work to store it in memory. Effective learning occurs when we can easily retrieve this information later. For example, when a teacher introduces a new concept in class, students use their working memory to process the information. If the concept is revisited and practiced, it moves into long-term memory, making it easier to recall in the future.
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: Cognitive learning encourages students to think deeply, analyze situations, and solve problems. This active engagement helps to strengthen neural connections, making the learning process more effective.
Linking New Knowledge to Existing Knowledge
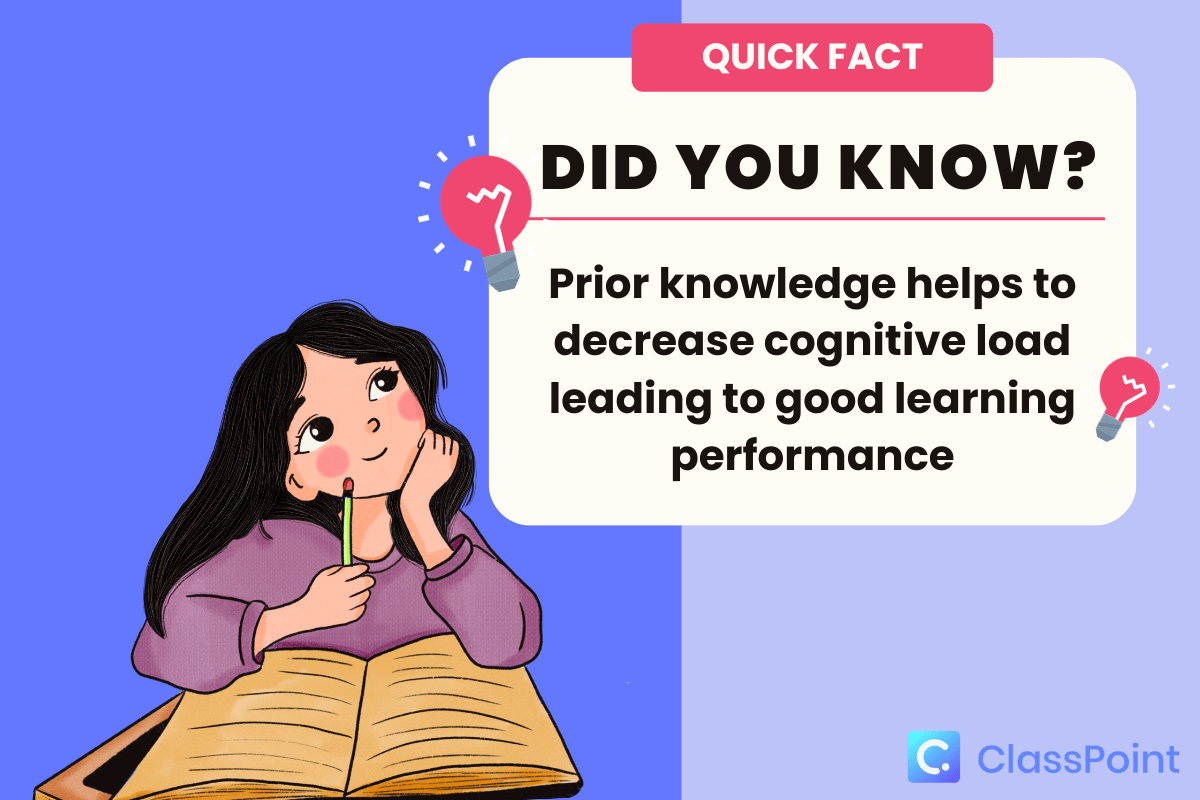
- One of the core principles of cognitive learning theory is the importance of connecting new information to what we already know. This is often referred to as building mental models or schemas. When students can relate new concepts to their existing knowledge, it creates a stronger, more durable memory.
Metacognition – Thinking About Thinking
- Metacognition plays a crucial role in cognitive learning. It involves being aware of one’s own learning process and strategies. Encouraging students to reflect on how they learn, what strategies work best for them, and where they need improvement, can lead to more effective learning outcomes.
The Role of Motivation and Engagement
- Motivation and engagement are key components of cognitive learning and developing higher order thinking skills. When students are motivated and engaged, they are more likely to invest effort in the learning process, leading to better outcomes.
Theory in Action: Cognitive Learning Examples
Cognitive learning theory isn’t just a collection of interesting ideas; it’s a practical tool that transforms classrooms and enhances learning. When put into action, it creates a dynamic and interactive environment that encourages students to engage deeply with the material.
Give this free interactive PowerPoint puzzle template and tutorial a try to encourage critical thinking!
Practical Examples of Cognitive Learning in the Classroom
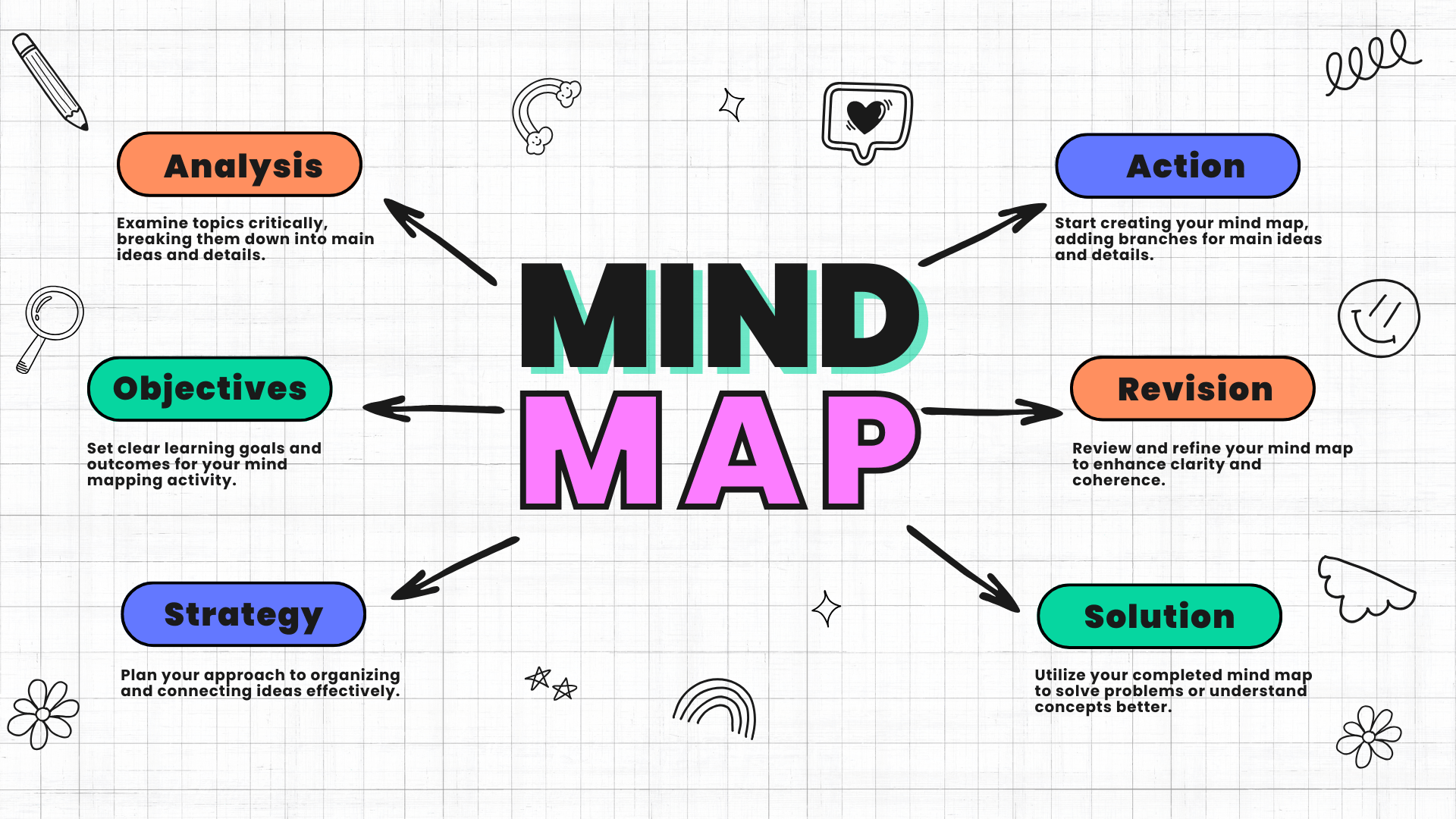
- Mind Mapping: Encourage students to use mind maps to organize their thoughts and ideas visually. This not only helps in retaining information but also in making connections between different concepts.
- Reflective Learning: Implement activities that encourage students to reflect on what they’ve learned, understand their learning process, and identify areas for improvement.
- Problem-Solving Activities: Encourage students to think critically and solve problems using their own knowledge and skills. This could be through puzzles, challenges, or real-life scenarios related to the lesson. It’s about getting those mental gears turning and encouraging students to think outside the box.
- Interactive Discussions: Create opportunities for students to discuss and debate topics, sharing their thoughts and ideas. This not only helps to cement their understanding but also allows them to learn from their peers.
Explore the 5 best mind mapping tools for teachers and students to get you started.
Cognitive Learning Theory Examples in Action
- Imagine a history teacher using storytelling and visual aids to bring historical events to life. Students are not just passive recipients of information; they’re actively engaged, visualizing the events, and making connections to the present day.
- A science teacher encourages students to conduct experiments, make predictions, and draw conclusions. This hands-on approach aligns perfectly with cognitive learning theory, promoting active engagement and deep understanding.
🌟 Enhancing Cognitive Learning in PowerPoint 🌟
You’ve heard of cognitive learning theory and its transformative power in the classroom. Now, let’s dive into how ClassPoint can elevate that experience right inside PowerPoint.
Imagine harnessing the principles of cognitive learning theory with cutting-edge tools designed to boost engagement, motivation, and interactivity while you are teaching with PowerPoint. Sound exciting? Let’s explore.
Presentation Tools for Enhanced Comprehension and Connections
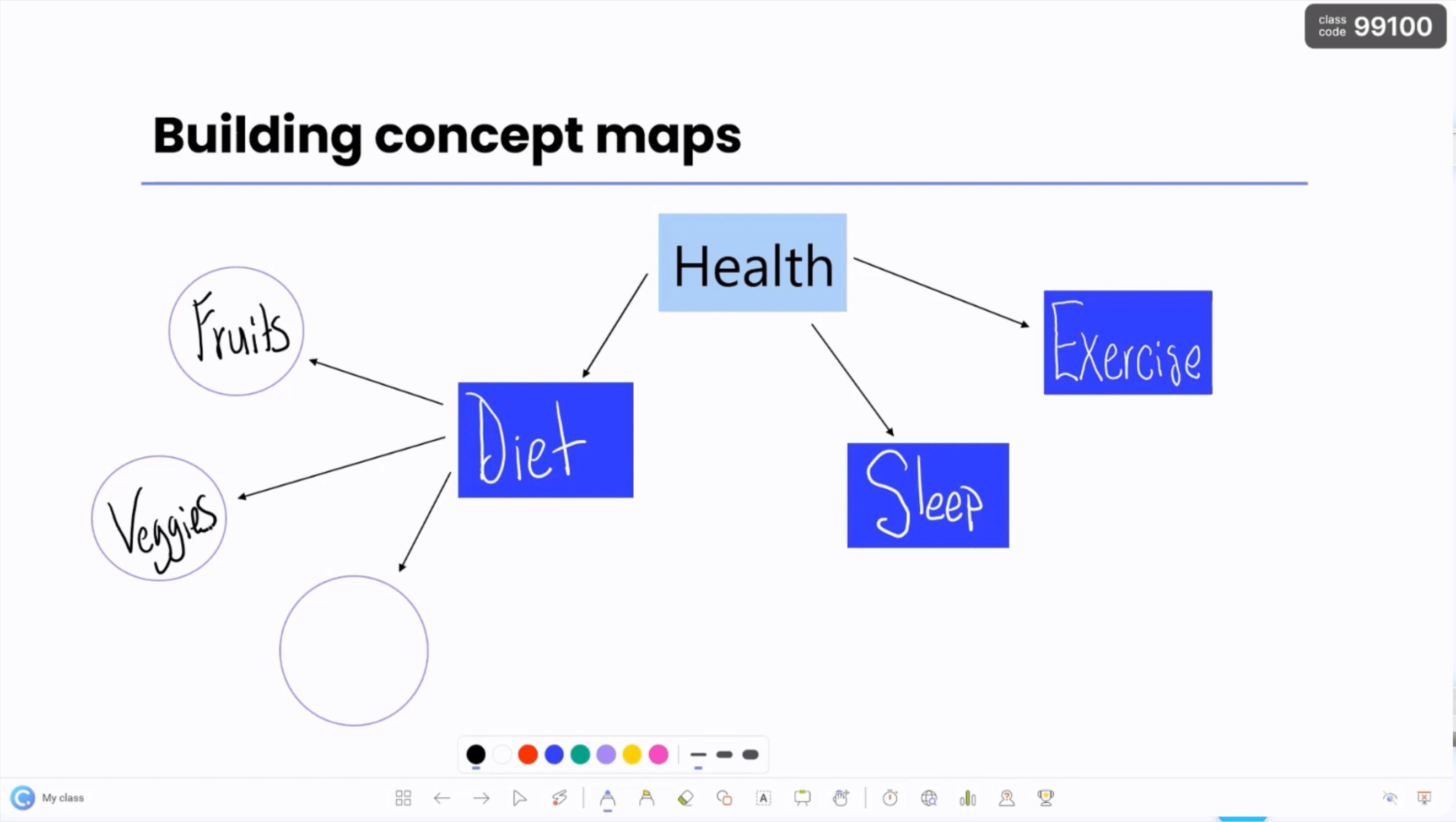
Imagine making your presentations a cognitive learning hotspot:
- Draft Interactive Mind Maps and Concept Maps: Use annotation tools and draggable objects to draft interactive mind maps and Concept Maps during slideshow mode, teaching students to organise their thoughts and arguments on-the-fly.
- Group Problem-Solving Activities: Run group problem-solving activities using Name Picker and Timer, organising students into groups and time the group activities.
- Teach Real-World Applications Right Inside PowerPoint: Enhance students’ understanding by swiftly accessing online articles or videos directly within your presentation, connecting abstract concepts to real-world applications and examples.
With all our Presentation Tools integrated into PowerPoint, efficiency meets effectiveness, ensuring that each presentation serves as a dynamic cognitive learning platform.
Interactive Quizzes for Amplified Retention and Engagement
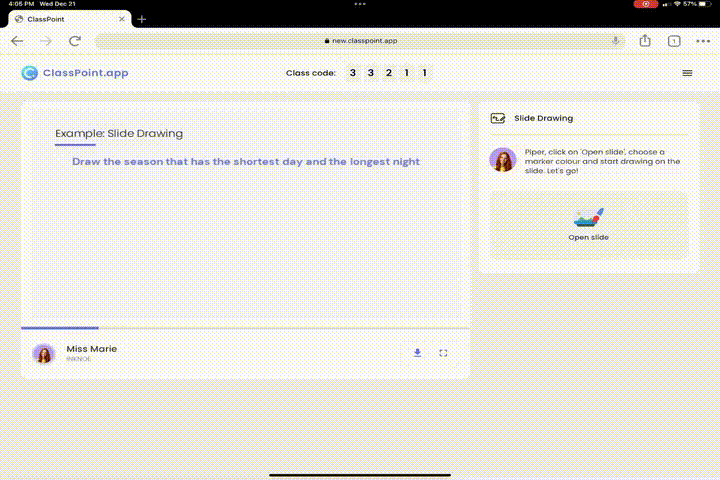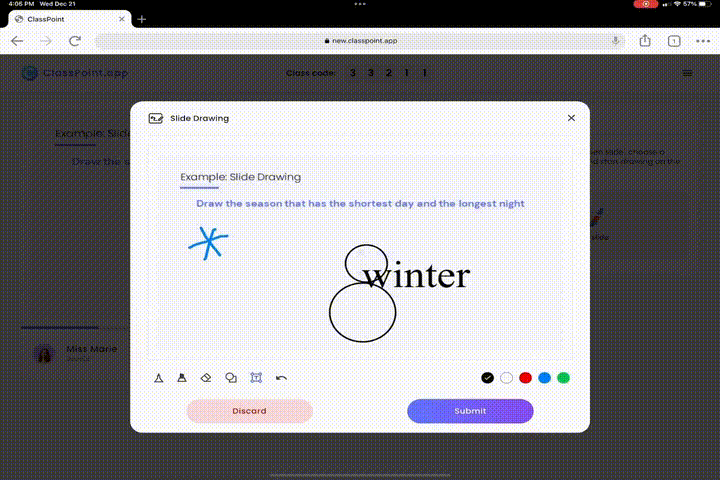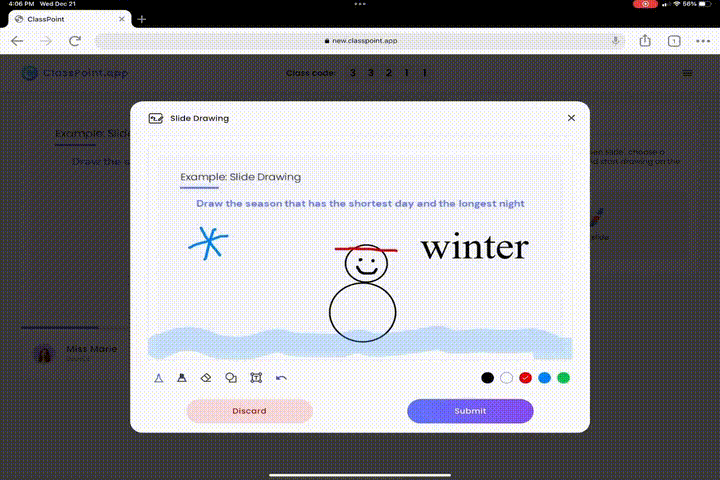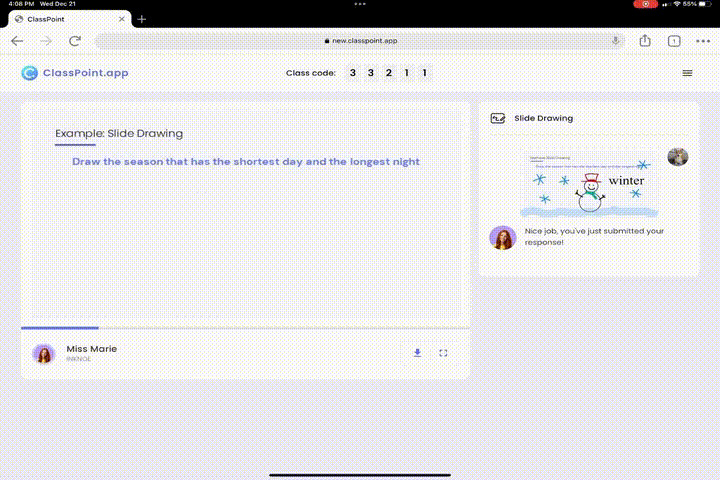
Testing doesn’t have to be mundane. Transform your slides into engaging cognitive learning exercises:
- Encourage Knowledge Retention with MCQ: Enhance recall and strengthen neural connections by employing Multiple Choice questions. Combined with Quiz Mode, teachers can and provide instant feedback and rewards that resonate with cognitive learning principles.
- Visual Learning Experience with Slide Drawing: Ignite creativity and stimulate cognitive development with Slide Drawing. This feature promotes active engagement, as students visually express their understanding, fostering a deeper connection with the material and enhancing their learning experience.
- Reflection and Progress Checking: Invite students to reflect on what they have learned with Interactive Quizzes or Quick Polls. These tools support cognitive learning by encouraging students to retrieve information, reinforcing knowledge and aiding long-term memory retention.
Integrating cognitive learning theory into presentations becomes effortless with ClassPoint. Its features, designed with modern pedagogical principles in mind, not only amplify engagement but also deepen understanding when combined with Interactive Quizzes.
Gamification Galore for Positive Reinforcements
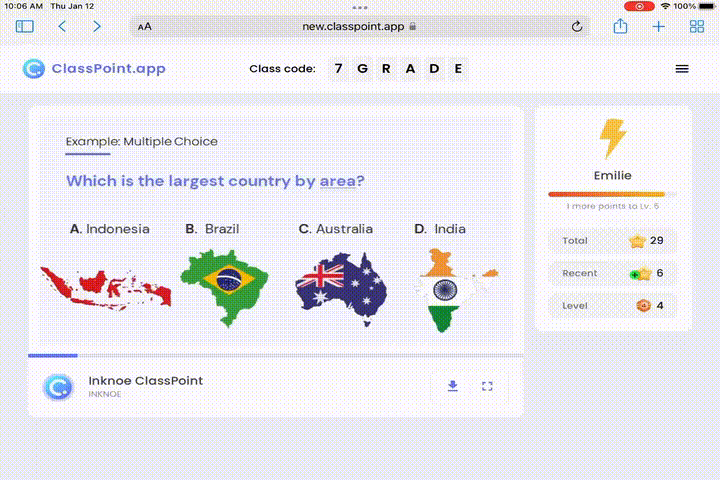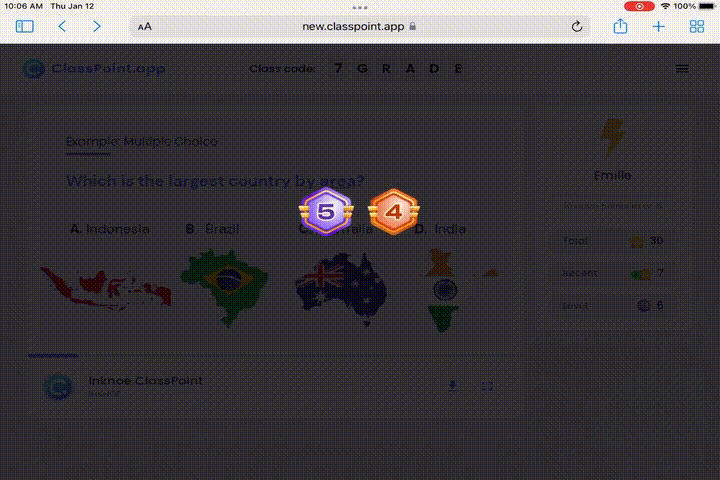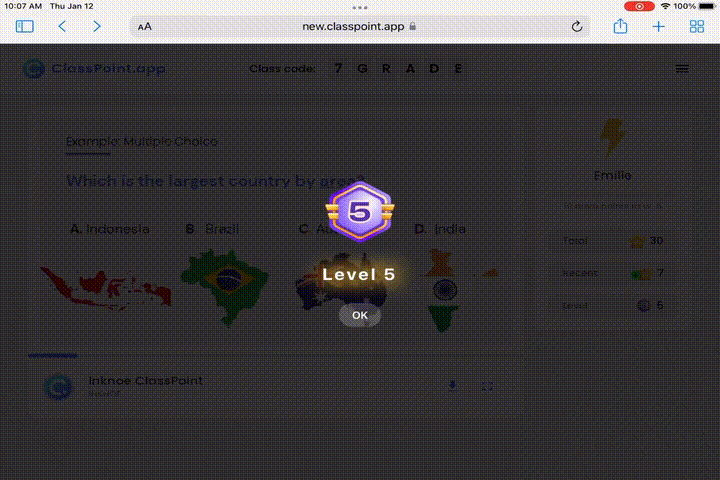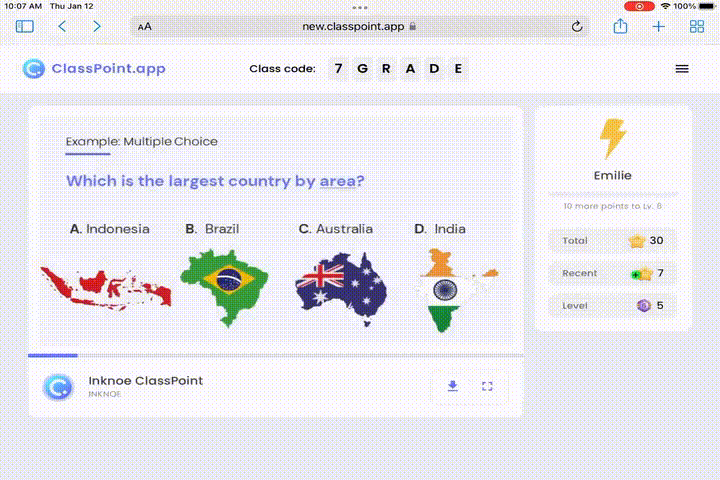
The essence of cognitive learning theory lies in making learning engaging and interactive. Here’s how ClassPoint’s gamification can supercharge this process:
- Rewards for Critical Thinking Activities: Teach critical thinking through debates. Use ClassPoint gamification tools to reward students for their arguments and points.
- Motivate through Leaderboard: Foster a sense of achievement and camaraderie by displaying a leaderboard of student accomplishments. This highlights dedication and effort, not just raw scores, promoting a healthy and motivating learning environment.
With tools like My Classes, educators can effortlessly track and manage student motivation, ensuring a tailored and impactful learning experience.
Social Cognitive Learning Theory: A Deeper Dive
So, you’ve grasped the basics of cognitive learning theory. But let’s zoom in on a particular branch that’s been making waves: Social Cognitive Learning Theory. It’s like the cool cousin of cognitive learning, adding a social dimension to the mix. This theory hinges on the idea that learning is not a solo journey; it’s a social endeavor.
Observation and Imitation: The Dynamic Duo
At the heart of social cognitive learning theory is the concept that we learn by watching others. Think of it as observational learning on steroids. Here’s the rundown:
- Modeling: You see someone doing something, and voila, you want to do it too! It could be a teacher solving a math problem or a peer presenting confidently. If they can do it, why can’t you?
- Imitation: After observing, comes the doing part. You try to replicate what you’ve seen. It’s not just about copying; it’s about understanding and applying.
The Bandura Influence
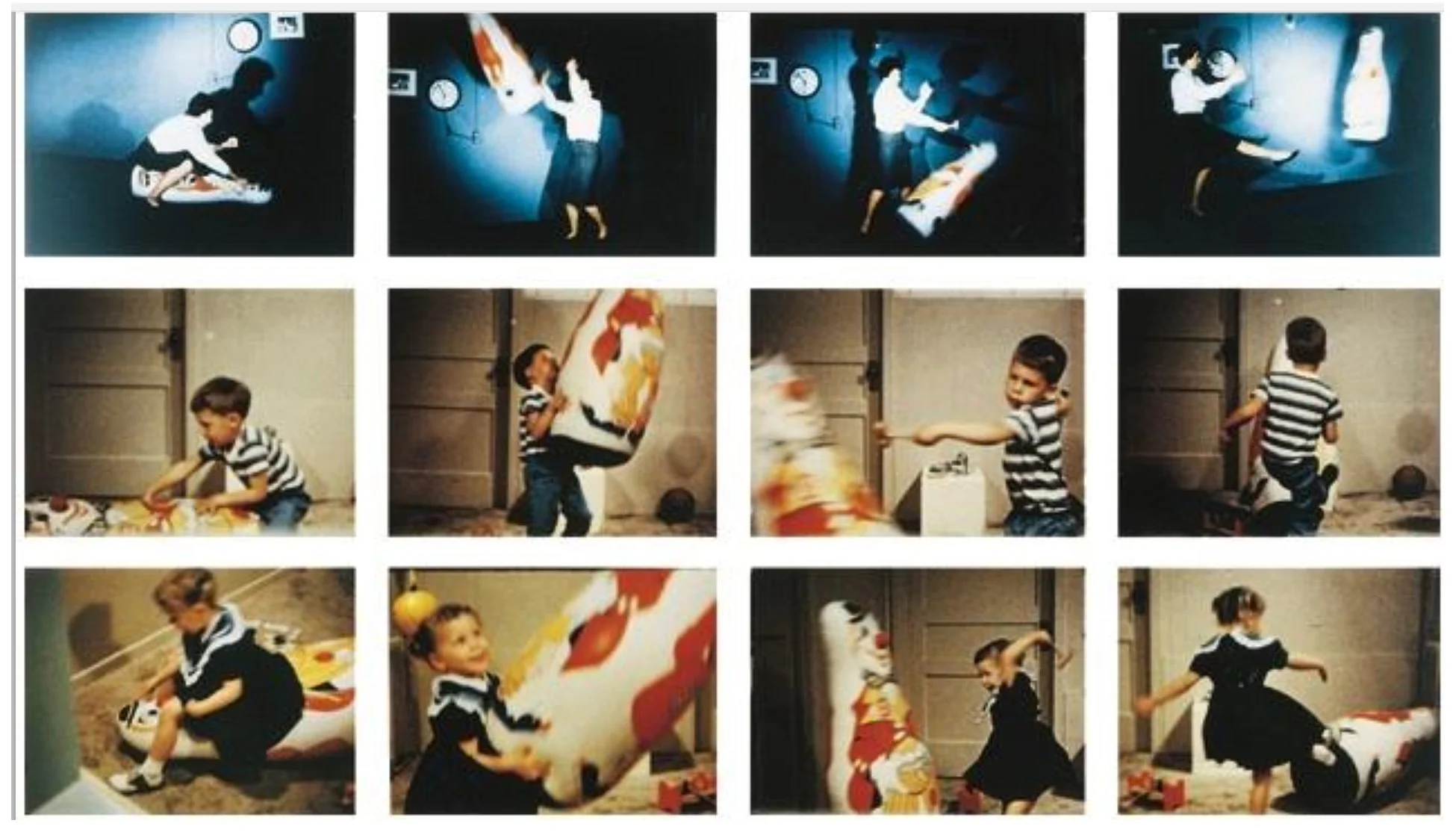

We can’t talk about social cognitive learning theory without giving a shoutout to Albert Bandura. His famous Bobo Doll experiment? A game-changer.
It showed that kids (and let’s be honest, adults too) learn by watching and imitating the actions of others. And it’s not just about mimicking actions; it’s about understanding the consequences and making choices.
Key Components to Keep in Mind
So, what makes social cognitive learning theory tick? Here’s the secret sauce:
- Attention: You’ve got to pay attention to learn. Whether it’s a mentor, a video, or a real-life scenario, your focus is crucial.
- Retention: Remembering what you’ve observed is next. If you can’t recall it, how can you apply it?
- Reproduction: This is where you put what you’ve learned into action. It’s showtime!
- Motivation: Last but not least, you need the drive to learn and apply. Positive reinforcements and understanding the value of what you’re learning play a big role here.
Why It Matters
Embracing social cognitive learning theory in the classroom means acknowledging the power of social influence on learning. It’s about creating an environment where students are not just passive receivers of information but active participants in their learning journey. So, ready to bring the social back into learning? Your classroom will thank you for it!
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is cognitive learning theory?
Cognitive learning theory revolves around the idea that learning is an active mental process. Learners use their cognitive abilities to comprehend, connect, and apply knowledge, making learning a thoughtful and intentional act.
How does social cognitive learning theory differ from cognitive learning theory?
While cognitive learning theory focuses on mental processes, social cognitive learning theory introduces a social element. It emphasizes learning through observing others, understanding that social interactions and environments play a significant role in the learning process.
Can you give me some practical examples of cognitive learning theory?
Certainly! Cognitive learning theory can manifest in various ways:
🧠 Problem-solving scenarios: Learners tackle complex problems, applying critical thinking and previous knowledge.
🧠 Concept mapping: Visual tools help in organizing and representing knowledge, fostering a better understanding.
🧠 Self-reflection: Learners review their own progress and strategies, adjusting their approach to learning as needed.
How can educators implement cognitive learning theory in the classroom?
Educators can:
🧠 Encourage critical thinking and problem-solving.
🧠 Promote the use of memory aids and mnemonics.
🧠 Utilize concept mapping for complex topics.
🧠 Foster a supportive learning environment that encourages questions and exploration.
What role does motivation play in cognitive learning theory?
Motivation is crucial. It drives learners to engage with material, persist through challenges, and take an active role in their own learning process. Without motivation, the desire to use cognitive skills for learning may dwindle.
Can technology enhance cognitive learning?
Absolutely! Technology like ClassPoint can bring gamification, interactive quizzes, and a variety of presentation tools into the classroom, aligning with cognitive learning principles and making learning more engaging and effective.
How does cognitive learning theory benefit learners in the long run?
Cognitive learning equips learners with skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to apply knowledge in various contexts. These skills are transferable and valuable, not just in academic settings but in real-life situations as well.
Take Your Teaching to the Next Level with ClassPoint
Understanding and applying cognitive learning theory can transform your teaching and significantly enhance student learning. Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, it’s time to put it into action.
Give ClassPoint a try for free, and experience firsthand how its interactive features can bring the principles of cognitive learning theory to life in your classroom. Embrace a teaching approach that not only educates but also engages and inspires. Start your journey today!